

In water and in a hydronium ion, the oxidation state of oxygen is also two. Alkali metals (except hydrogen) remove one electron to form +1 ion. We may provide many examples of such compounds among salts, acids, oxides and bases: KClO₄, H₂SO₄, N₂O₃, NaOH etc. As this non-metal is a strong oxidizer, it frequently displays this oxidation state in compounds. The oxidation number describes explicitly the degree to which an element can be oxidized (lose electrons) or reduced(gain electrons). The lowest oxidation state of oxygen is -2. Oxygen is capable of displaying several oxidation states in chemical reactions: -2, -1, 0, +2. 1 Comparing Sublevels of the Groups SG 6 chemistry oxidation numbers and. Oxygen is a strong oxidizer (only fluorine displays stronger oxidation properties because of its greater electrical negatively and its more pronounced non-metallic properties (by its position in the periodic table)). This element is found in group 15 and period 2 of the Periodic Table of the. In its compounds, chromium is found in the +2, +3, and +6 oxidation states, with the +3 oxidation state being the most stable and the most common. The elements are arranged in an ascending order of their atomic numbers forming a table of 18 vertical columns and 7 horizontal periods, To indicate the type of the element: S, P except zero-group is a representative element or main group element, zero group is a noble gas, d is the main transition element, and f is the inner transition element. It is encountered in the form of 3 isotopes – in nature, oxygen with the atomic numbers of 16, 17 and 18 is encountered. The elements are arranged in seven horizontal rows. The periodic table, also known as the periodic table of the (chemical) elements, is a tabular display of the chemical elements.It is widely used in chemistry, physics, and other sciences, and is generally seen as an icon of chemistry. Each box represents an element and contains its atomic number, symbol, average atomic mass, and (sometimes) name. It supports breathing, combustion and decomposition. A modern periodic table arranges the elements in increasing order of their atomic numbers and groups atoms with similar properties in the same vertical column ( Figure 2.26 ). All alkaline earth elements have an oxidation number of. Oxygen is a diatomic colorless gas without smell or taste. The alkaline earth elements are metallic elements found in the second group of the periodic table.
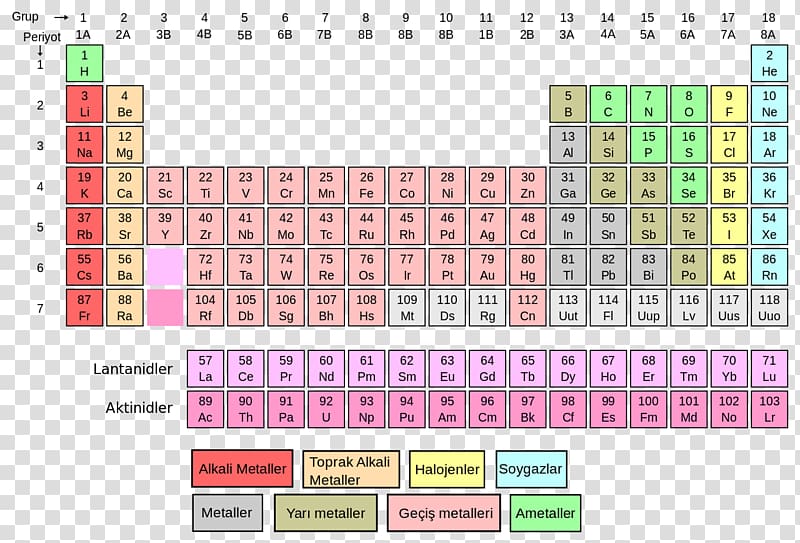
It is a representative of the chalcogens group (they also include sulfur, selenium, tellurium and polonium).

Oxygen is an element of the 6ᵗʰ group (under the new classification the 16ᵗʰ group) of the main subgroup of the periodic table.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
